RXBio Translates Sequence to Science and Industry
Tel: 027-87050299Email: sales@rxbio.cc
- Home
- Single-cell Sequencing
- Spatial Transcriptomics
- Third-generation Sequencing
- Omics Technologies
- Bioinformatics
- Experimental Platform
- About US
中文
RXBio Translates Sequence to Science and Industry
The Co-IP (Co-Immunoprecipitation) method is a classic technique for studying protein-protein interactions, as it detects whether there is a specific interaction between two protein molecules in vitro. Its principle is to use a target protein-specific antibody to indirectly capture the proteins bound to the specific target protein, thereby identifying high-confidence interacting proteins of the target protein.
✔ High protein reliability
✔ Verifiable authenticity
The differentiation of osteoblasts is a dynamic process regulated by spatiotemporal genetic programs. During this process, cytoskeletal proteins not only participate in the alteration of the cytoskeleton but also regulate multiple signaling pathways, including Wnt, Hedgehog, MAPK, and so on.
The microtubule-actin crosslinking factor MACF1 is a multi-domain cytoskeletal protein that is widely involved in physiological processes such as cytoskeleton assembly, cell migration, proliferation, and differentiation.
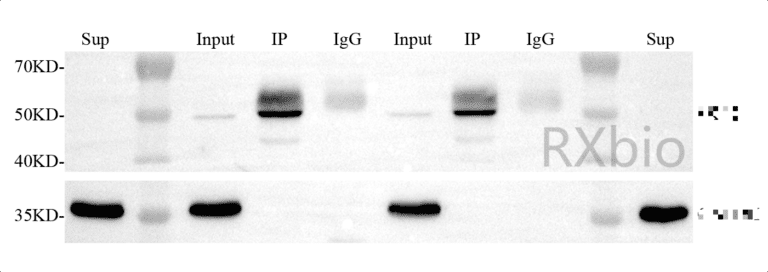
Our cooperative client published a paper titled “MACF1 promotes osteoblast differentiation by sequestering repressors in cytoplasm” in “Cell Death & Differentiation”. This study discovered for the first time that the cytoskeletal protein MACF1 affects the differentiation of osteoblasts by influencing the localization of transcription factors related to osteogenic differentiation in cells. We provided transcriptome sequencing technology, Co-IP combined with protein mass spectrometry technology, and ChIP-seq technology to help the researcher finally identify the interacting proteins of MACF1 and its regulatory mechanism.
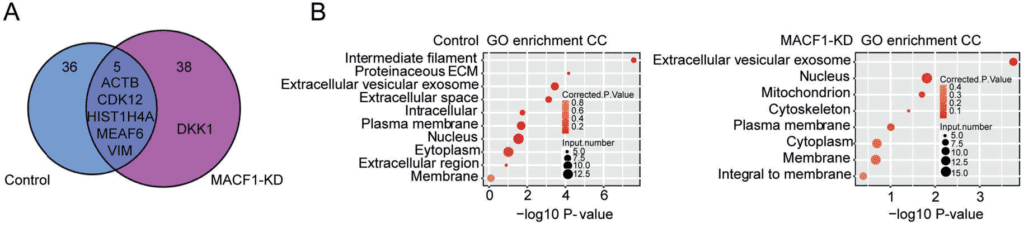
Among them, in order to further study the role of MACF1, the research group utilized co-immunoprecipitation combined with protein mass spectrometry analysis (Co-IP-MS) to detect the proteins that interact with MACF1 before and after MACF1 knockdown. The results showed that five proteins were present in both the knockdown group and the control group cells, indicating that these five proteins (ACTB, CDK12, HIST1H4A, MEAF6, VIM) interact with MACF1. Enrichment analysis was performed on the interacting proteins in the knockdown group and the control group. The results showed that the proteins interacting in the control group were mainly enriched in the filament and extracellular matrix pathways, while the genes were mainly enriched in the nucleus pathway after MACF1 knockdown.