introduction
The cell cycle refers to the entire process that a cell undergoes from the completion of one division to the end of the next division, which is divided into two stages: the interphase and the mitotic phase. The interphase is further divided into the G0 phase, G1 phase, S phase, and G2 phase; the mitotic phase is the M phase.
– G0/G1 phase: During the G1 phase, the cell volume gradually increases, and the cell begins to synthesize RNA and proteins while the DNA content remains in a diploid state. The G0 phase is a stage where the cell temporarily stops dividing and exits the cell cycle. However, under certain appropriate stimuli, it can re-enter the cycle. It is impossible to distinguish between the G0 and G1 phases based on DNA content.
– S phase: In this stage, the synthesis of DNA is completed, as well as the synthesis of histones related to the assembly of DNA to form chromatin. The DNA content increases during this period, ranging between the G1 and G2 phases, and the DNA content in the cell nucleus is between diploid and tetraploid.
– G2/M phase: The G2 phase is the gap between the end of DNA replication and the start of mitosis. When the DNA replication results in a tetraploid state, the cell enters the G2 phase. Cells in the G2 phase continue to synthesize RNA and proteins until they enter the M phase. Similarly, it is impossible to distinguish between the G2 and M phases based on DNA content.
The most commonly used method for detecting the cell cycle is to detect the cell’s DNA content (the technical principle of the PI/RNase staining method). Cells that are growing normally will all go through the division process. The G0/G1 phase is the diploid stage. During the S phase, DNA synthesis begins, and the DNA content is between diploid and tetraploid. By the G2/M phase, the cell is in the tetraploid stage. After that, the cell divides into two and enters the next cell cycle.
Propidium iodide (abbreviated as PI) is a fluorescent dye for double-stranded DNA. After propidium iodide binds to double-stranded DNA, fluorescence can be generated, and the fluorescence intensity is proportional to the content of double-stranded DNA. After the intracellular DNA is stained with propidium iodide, the DNA content of cells can be measured using a flow cytometer. Then, based on the distribution of DNA content, the cell cycle can be analyzed. Since PI can bind to both DNA and RNA, RNase should be used to digest RNA.
advantages
✔ Strict controls and experimental quality control points to ensure the accuracy and reliability of the results.
✔ Data analysis, graphing and English materials and methods, along with detailed raw data, will safeguard the authenticity of your data and facilitate your article publication.
workflow

Delivery Contents:
A. Raw data of all experimental results.
B. Experimental reports (including detailed experimental procedures and the manufacturer and catalog number information of the main instruments and reagents).
C. English materials and methods.
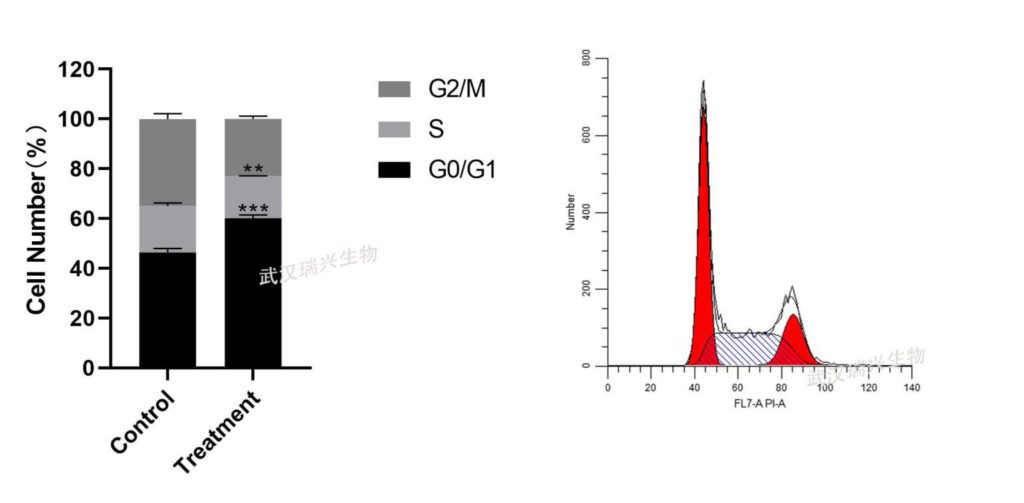
demo data