RXBio Translates Sequence to Science and Industry
Tel: 027-87050299Email: sales@rxbio.cc
- Home
- Single-cell Sequencing
- Spatial Transcriptomics
- Third-generation Sequencing
- Omics Technologies
- Bioinformatics
- Experimental Platform
- About US
中文
RXBio Translates Sequence to Science and Industry
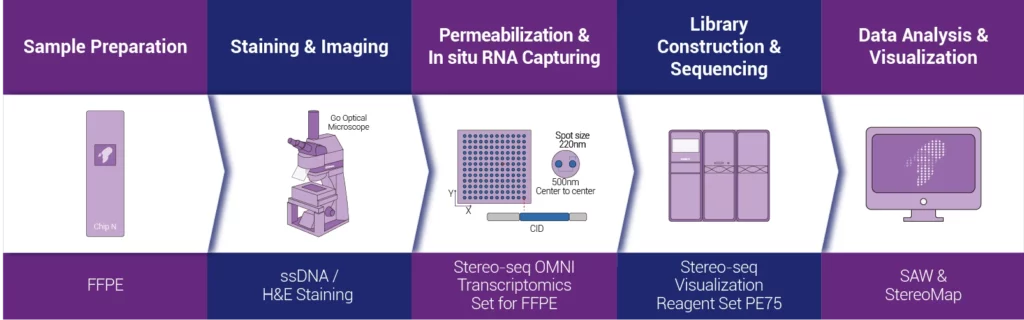
The Stereo-seq FFPE product solution for spatial transcriptomics uses “random probes” with spatial coordinate information to conduct in-situ capture of Total RNA molecules within the tissue cells of FFPE samples. And it restores them back to their spatial positions through spatial barcodes (Coordinate ID, CID), achieving the construction of a whole-transcriptome spatial expression atlas with single-cell resolution. Users can perform H&E staining or nuclear staining on the same tissue slice according to research needs and purposes. Combined with powerful analysis tools, they can flexibly carry out multi-modal data analysis at the single-cell level resolution, helping clinical scientific research to gain a deeper understanding of the occurrence and development mechanisms of diseases.
01 | H&E or nuclear staining on the same slice.
According to research requirements, H&E staining or nuclear staining can be chosen to be carried out on the same tissue slice, so as to achieve multi-modal data acquisition and integrated analysis.
02 | Spatial single-cell analysis
The detection resolution reaches 500 nm, enabling spatial single-cell level analysis.
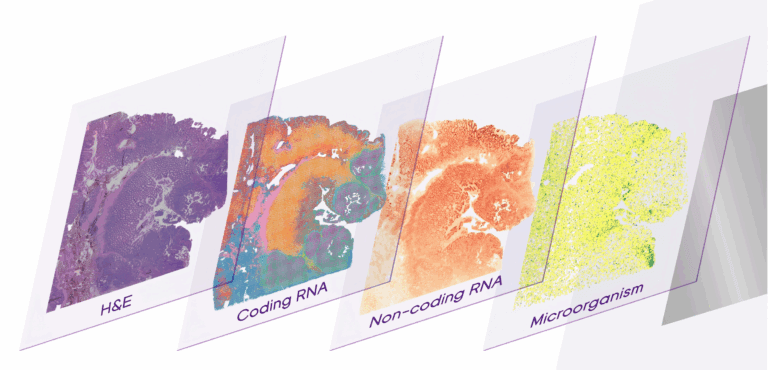
03 | Co-capture of coding and non-coding RNA.
Based on the technical principle of random probes, in-situ capture of both mRNA and non-coding RNA can be achieved simultaneously.
04 | Co-detection of microorganisms and hosts.
It can simultaneously capture the spatial expression information of microorganisms and their hosts, and then explore the interaction relationship between hosts and microorganisms.
05 | There is no species limitation.
It can not only be applied to humans and mice, but also be used to explore spatio-temporal omics information of samples from other species.
01 Accurately depict the spatial distribution of multiple types of cells.
Based on the spatial information of gene expression in FFPE samples, annotate multiple cell types and accurately locate the spatial distribution of various cell types.
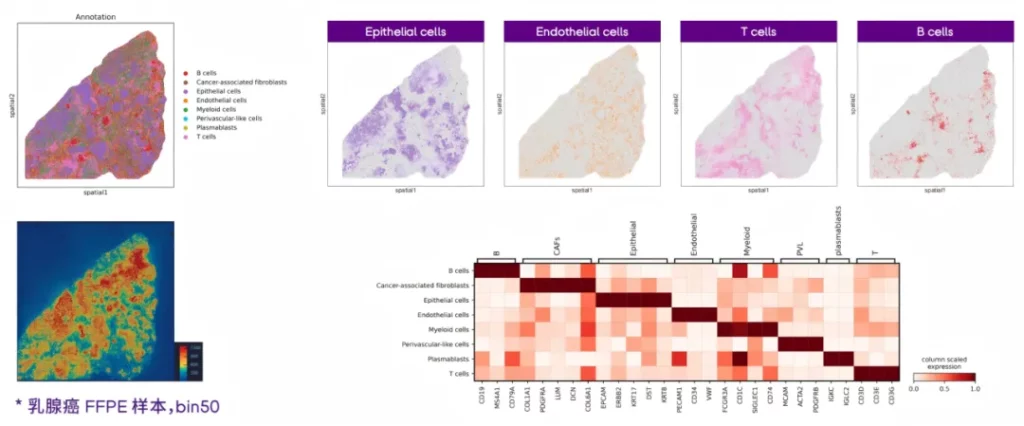
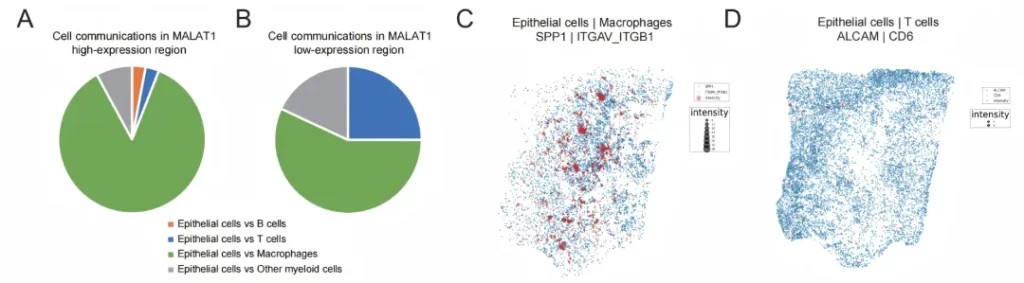
02 Explore the immune characteristics of cancer tissues.
Tissue typing is performed based on the histological information provided by H&E, so as to further explore the spatial molecular characteristics of the precancerous areas and cancerous areas.
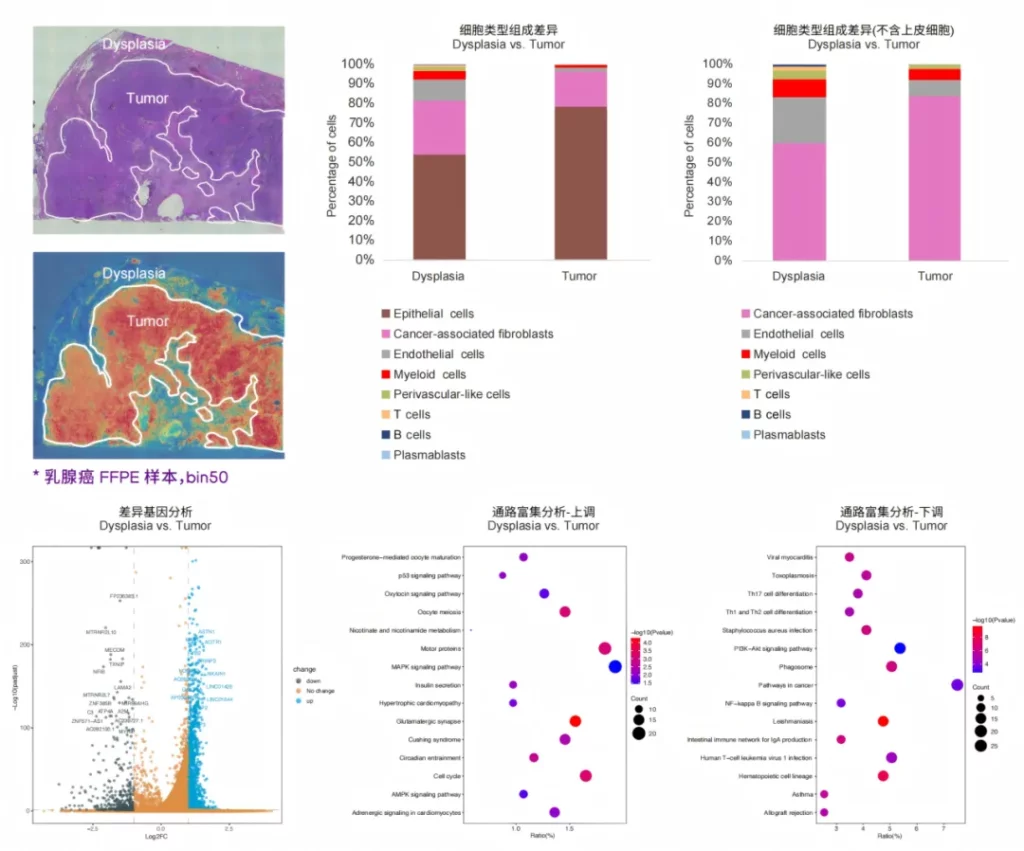
03 Co-detection of microorganisms and hosts.
The spatial transcriptome detection data of Mycobacterium tuberculosis (Mtb) in the infected mouse lung samples are consistent with the results of pathological staining.
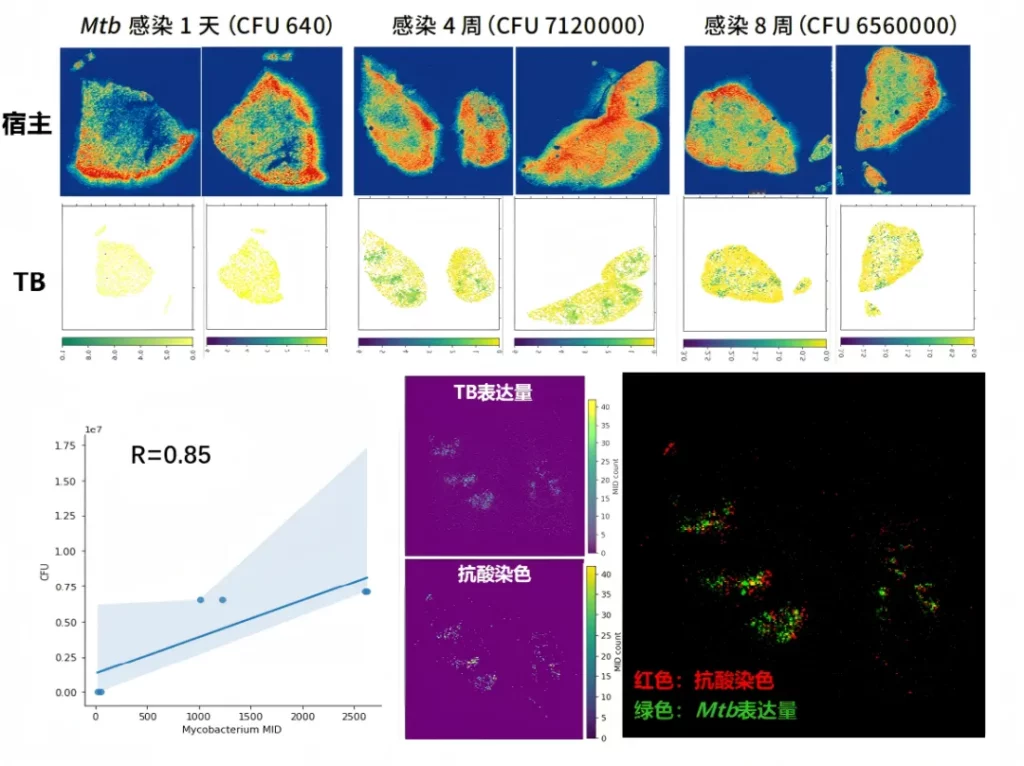
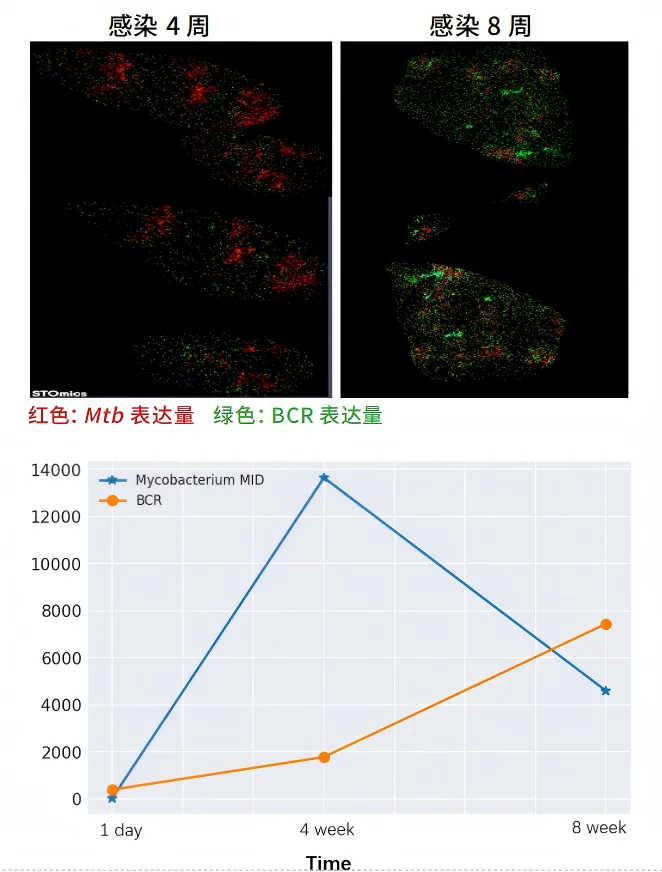
04 Conduct high-resolution spatial analysis of mRNA and lncRNAs simultaneously.
In human lung cancer tissue samples, co-capture analysis of coding and non-coding RNA is achieved, and the tumor immune microenvironment is accurately analyzed in combination with non-coding RNA.
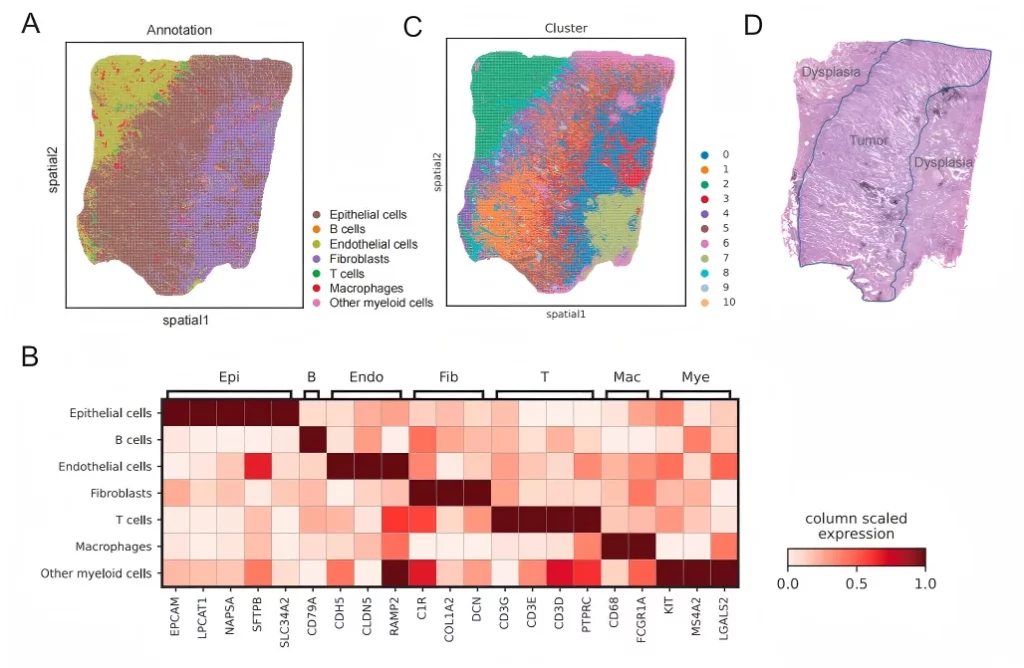
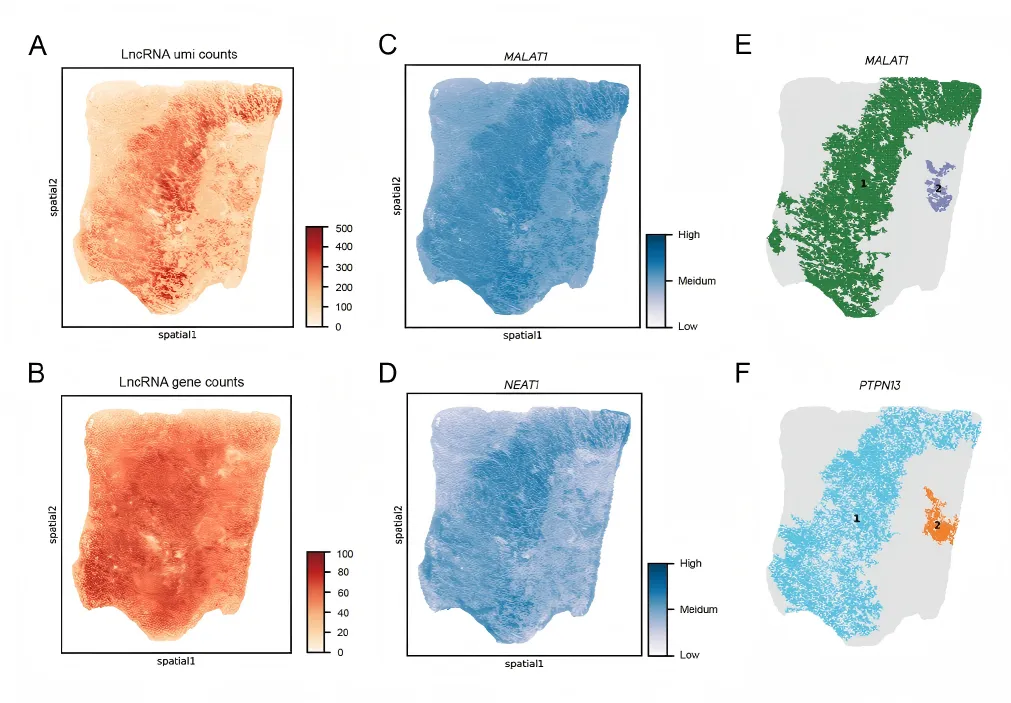
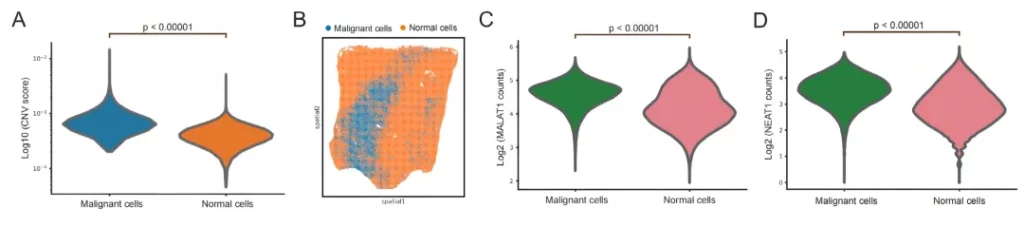
空间可变lncRNA与恶性细胞存在空间相关性